1. What are camera aluminum die-casting parts? What are their advantages?
As photographic equipment increasingly moves towards lightweight, high-strength, and high-precision designs, the materials and manufacturing processes of camera structural components are also gradually changing. Among many processing methods, aluminum die-casting is widely used in the manufacturing of key components such as camera bodies, lens housings, brackets, and heat sinks due to its high efficiency, high precision, and excellent material properties. So, what are camera aluminum die-casting parts? What are the core advantages of these components?
(1) What are camera aluminum die-casting parts?
Camera aluminum die-casting parts refer to camera structural and functional components manufactured from aluminum alloy materials using the die-casting process. Die-casting is a process that involves rapidly injecting molten aluminum liquid into a precision mold under high pressure, and then cooling and shaping it to obtain high-precision metal parts. Because aluminum alloy has high strength, light weight, good thermal conductivity, and is easy to process, it has become one of the mainstream structural materials in the camera manufacturing industry.
Common aluminum die-casting parts in cameras include:
Camera body housing
Lens housing and optical support components
Internal fixing structures (such as brackets, frames, base plates)
Heat dissipation components and thermal bases
Mounting supports, guide rails, and connectors
These components are not only the foundation of the camera's structural strength but also an important guarantee for stable shooting, precise focusing, and reliable heat dissipation.
(2) Core advantages of camera aluminum die-casting parts
Camera aluminum die-casting parts have significant advantages in performance, reliability, and design flexibility. These characteristics make them widely used in professional cameras, action cameras, industrial cameras, drone photography equipment, and other fields.
Advantage 1: Improved lightweight performance and significantly enhanced portability
Cameras require not only high-strength structures but also the lightest possible overall weight.
Aluminum alloy has only one-third the density of steel, but its strength is sufficient to meet the load-bearing requirements of camera housings and internal structural components.
The advantages of lightweight design include:
Less effort required for handheld shooting over extended periods
Reduces the overall burden on the camera, improving the user experience
Especially suitable for action cameras, travel cameras, and drone photography equipment
This "lightweight but sturdy" performance makes aluminum die-casting parts an indispensable material choice in camera design.
Advantage 2: High-Precision Molding, Meeting the Complex Structural Requirements of Cameras
Cameras have high structural precision, with many internal components being small and complex. Die-casting technology allows for one-time molding using a mold, ensuring:
High dimensional consistency
Excellent surface flatness
Complex structures require no multiple processing steps
High production efficiency, suitable for mass manufacturing
In addition, die-casting molds can achieve precision control at the 0.01mm level, allowing aluminum die-cast parts to perfectly match optical and electronic systems.
Advantage 3: Sturdy and Durable, Enhancing the Overall Lifespan of the Camera
Photography equipment is often used outdoors and may encounter vibrations, drops, temperature changes, and humid environments.
Aluminum alloy possesses excellent mechanical strength and corrosion resistance, making the camera more resistant to:
Daily wear and tear
Accidental drops
Environmental corrosion
Fatigue damage caused by long-term use
This is why many professional cameras, industrial cameras, and high-end lenses use aluminum alloy structural components instead of plastic parts.
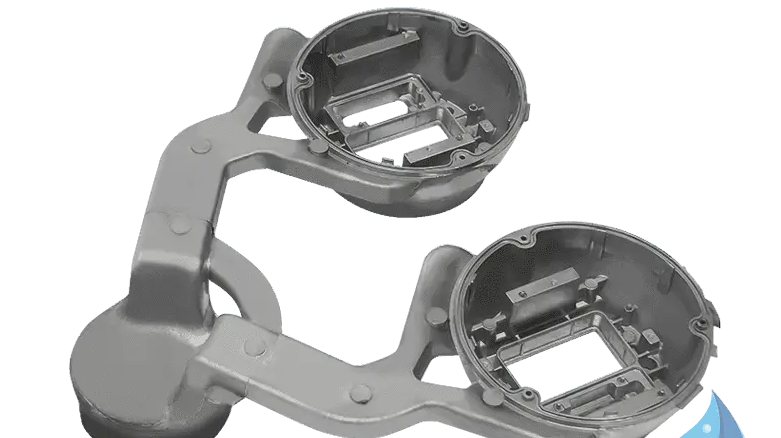

Advantage 4: Excellent Heat Dissipation Performance, Protecting Sensors and Electronic Components
Modern cameras are equipped with:
High-pixel CMOS/CCD sensors
High-performance image processors
Stable power supply modules
These core electronic components generate a significant amount of heat during long periods of shooting or continuous 4K and 8K video recording.
Aluminum die-cast parts have excellent thermal conductivity and are often used in:
Sensor heat dissipation bases
Heat dissipation frames inside lenses
Camera body heat dissipation areas
Rapid heat dissipation reduces noise, lowers temperature rise, extends the lifespan of camera electronic components, and improves equipment stability.
Advantage 5: Strong Aesthetic Appeal
After surface treatments such as spraying, oxidation, and electrophoresis, the aluminum alloy surface can exhibit a high-end metallic texture, significantly enhancing the camera's appearance.
Consumers generally have a higher appreciation for metal bodies, including:
Better feel
Stronger texture
More professional image
Advantage 6: Design Freedom, Supporting Complex Structures
Die-casting technology allows for the integration of multiple structures into a single part, such as:
Studs
Guide rails
Hollow designs
Connecting grooves
Heat dissipation fins
This means that structures that would originally require multiple parts to assemble can be combined into a single integral part, improving the overall stability of the camera while reducing production costs.
Advantage 7: High Production Efficiency
Aluminum die casting is suitable for mass production and offers the following advantages:
Fast molding speed
Long mold life
Controllable unit cost
Good batch consistency
For consumer and professional camera product lines, this highly efficient production method effectively reduces manufacturing costs and shortens delivery cycles.
(3) Why is the camera manufacturing industry increasingly relying on aluminum die-cast parts?
As photographic equipment develops towards "high heat dissipation, high precision, lightweight, and high stability," aluminum die-cast parts provide the most cost-effective material option. They meet high strength requirements, enable precise manufacturing of complex structures, and support high-end appearance design and rapid heat dissipation needs.
Compared to plastic parts, they are more durable and professional; compared to CNC machined parts, they are lower in cost and have higher production efficiency. Considering overall performance, aluminum die-cast parts have become an indispensable core process in modern camera manufacturing.
2. What are some common problems with camera aluminum die-casting parts?
Camera aluminum die-casting parts, as important structural components of photographic equipment, are widely used in camera bodies, lens barrels, internal support frames, heat dissipation structures, mounting bases, and other parts. Because cameras have extremely high requirements for precision, stability, and appearance, aluminum die-casting parts may encounter various quality or performance problems during production and use. Understanding these problems will not only help in choosing more reliable suppliers but also help camera manufacturers mitigate risks during the design and production stages.
(1) Structural Problems
1) Dimensional deviations and unstable precision
The internal space of a camera is compact, and many structural components require precise fitting. Dimensional deviations can lead to assembly difficulties or loosening problems.
Common causes include:
Unreasonable mold design
Unstable die-casting temperature control
Insufficient aluminum liquid filling
Mold wear leading to dimensional changes
This problem is most common in lens housings, guide rails, and guiding structures.
2) Uneven wall thickness leading to insufficient strength
Camera structural components often use lightweight thin-walled designs, but uneven wall thickness distribution can cause:
Weak points under stress
Easy deformation during use
Deformation of the lens barrel during tightening
These problems are often related to mold runner design and die-casting process parameters.
(2) Appearance Problems
1) Surface pores, sand holes, and shrinkage cavities
Camera housings and lens barrels have extremely high appearance requirements, and surface defects in aluminum die-casting parts can lead to:
Uneven coating
Changes in metal texture
Reduced structural strength
Lowered product quality
Common defects include:
Pores (caused by air entrapment)
Sand holes (uncleaned slag)
Shrinkage cavities (caused by uneven material cooling)
These problems directly affect the visual quality of the housing.
2) Surface roughness, flow marks, and water marks
These surface problems become more obvious after painting or oxidation, affecting appearance consistency.
Main reasons include:
Unstable aluminum liquid flow speed
Excessive cooling speed
Uneven mold temperature
For high-end camera housings, surface defects are unacceptable.
(3) Performance-Related Issues
1) Insufficient Heat Dissipation
The higher the degree of digitalization of the camera, the more important heat dissipation becomes; however, if there are pores or coarse grains inside the aluminum die-casting part, it will affect the thermal conductivity.
Common manifestations:
Temperature rises too quickly after prolonged video recording
Increased sensor noise
Premature triggering of automatic shutdown protection
This is usually related to material quality and die-casting density.
2) Insufficient Strength or Internal Inclusions
If the aluminum die-casting part contains internal impurities, cracks, or slag inclusions, it may lead to:
Reduced drop resistance of the casing
Deformation of lens structural components
Fatigue cracks after long-term use
Lens structural components are particularly sensitive because they need to maintain long-term geometric stability.
3) Corrosion or Poor Surface Treatment Adhesion
If the surface of the die-casting part contains oil, oxidation, or impurities, it will lead to:
Paint peeling
Uneven color of the oxide film
Pitting corrosion after long-term use
Cameras are often used outdoors, so surface treatment issues are particularly critical.
4. Process-Related Issues
1) Deformation and Warping Problems
Thin-walled structures are prone to deformation after cooling, such as:
Oval deformation of the lens housing
Unevenness of the camera body back panel
Slight twisting of the support frame affecting assembly
Reasons include uneven cooling and unbalanced mold ejection force.
2) Difficulties in Secondary Processing (such as CNC precision machining)
Aluminum die-casting parts usually require secondary processing, such as threading, precision milling, and drilling.
Reasons for processing difficulties may include:
Internal pores causing chipping during processing
Uneven material density affecting tool life
Improper control of die-casting allowance leading to processing deformation
This will significantly increase production costs and scrap rate.
(5) Assembly and Usage Issues
1) Unsuitable Assembly Tolerances
Camera structural components require extremely high tolerance matching. Large dimensional deviations in die-cast parts can lead to:
High assembly resistance
Interference or looseness
Screw hole misalignment affecting assembly
Assembly difficulties directly impact production efficiency.
2) Resonance or Noise During Use
If some internal structural components are poorly designed or lack sufficient processing precision, it can lead to:
Slight resonance during focusing
Vibration transmission affecting stability
Mechanical noise during video recording
These problems affect the professional performance of the camera.
Because cameras are high-precision devices, they require extremely high accuracy, strength, and stability for every structural component. Therefore, when selecting suppliers and inspecting processes, special attention must be paid to every aspect of the product. Only by strictly controlling every stage of production can we ensure that camera aluminum die-casting parts meet industry requirements and provide stable, durable, and reliable structural support for lenses and cameras.
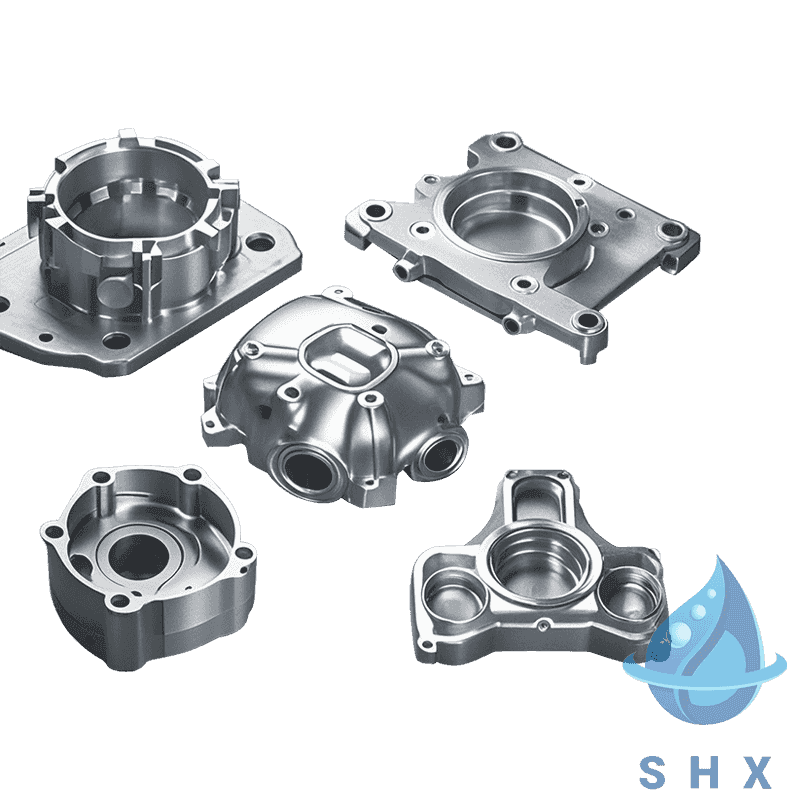
Table summarizing common problems, cause analysis, and solutions for camera aluminum die-casting parts:
| Common Problems | Possible Causes | Solutions |
| Surface Porosity/Shrinkage Cavities | 1. Incomplete gas venting during die casting 2. Mold temperature too high or too low 3. Impurities in the aluminum alloy or poor fluidity |
1. Optimize mold venting design 2. Control mold temperature (usually 180-250℃) 3. Use high-purity aluminum material and improve the casting process |
| Cracks or Cold Shuts | 1. Insufficient aluminum alloy temperature 2. Mold cooling too fast 3. Insufficient die casting pressure or speed |
1. Increase aluminum alloy pouring temperature (650-720℃) 2. Adjust mold cooling rate 3. Increase injection pressure or speed |
| Dimensional Deviations | 1. Mold wear or deformation 2. Incorrect shrinkage rate calculation 3. Inaccurate post-processing positioning |
1. Regularly repair or replace the mold 2. Recalibrate the shrinkage rate (usually 0.5-0.7% for aluminum die castings) 3. Optimize machining datum |
| Surface Burrs or Flash | 1. Insufficient mold clamping force 2. Mold parting surface wear 3. Decreased die casting machine accuracy |
1. Increase clamping force or adjust clamping parameters 2. Repair the mold parting surface 3. Inspect the die casting machine guide rails or hydraulic system |
| Internal Porosity (Poor Airtightness) | 1. Uneven solidification shrinkage of the aluminum alloy 2. Insufficient die casting feeding 3. Excessive impurities (such as aluminum oxide) |
1. Optimize gate and cooling system design 2. Increase the pressurization and feeding stage 3. Degassing and slag removal treatment during melting |
| Difficulty in Demolding | 1. Insufficient mold draft angle 2. Rough mold surface or no release agent applied 3. Ejector mechanism malfunction |
1. Increase the draft angle (usually 1-3°) 2. Polish the mold and use release agent correctly 3. Inspect the ejection system |
| Failure to Meet Mechanical Performance Standards | 1. Aluminum alloy composition is substandard (e.g., unbalanced Si/Mg ratio) 2. Improper heat treatment process 3. Excessive cooling rate |
1. Strictly inspect raw material composition |
3. Why do camera accessory manufacturers prefer aluminum die-casting?
In the camera industry, aluminum die-cast parts play a very important role, whether it's for camera bodies, lens accessories, internal structural brackets, or heat dissipation components. As cameras evolve towards lightweight design, high strength, high precision, and good heat dissipation, aluminum die-casting has gradually become the mainstream manufacturing method. Its widespread adoption stems from its outstanding advantages in design flexibility, production efficiency, and material performance. Below, we will analyze from multiple perspectives why camera accessory manufacturers are increasingly favoring aluminum die-casting.
(1) Lightweight and High Strength
Camera equipment, especially portable cameras, action cameras, and drone camera equipment, all have strict weight requirements. Aluminum alloy has low density and light weight, yet possesses good mechanical strength and toughness, perfectly meeting the lightweight requirements of camera accessories.
Compared with plastic materials, aluminum die-cast parts are more robust and reliable; compared with steel or other metals, aluminum die-cast parts have advantages in weight and cost. It can provide the necessary protection and structural support for the camera without adding extra burden.
(2) Strong Forming Capability
The internal structure of a camera is compact and multi-layered, with many structural parts having complex shapes, requiring high precision and consistency. The aluminum die-casting process allows for one-time molding through a mold, significantly reducing processing steps and ensuring that the dimensional accuracy, flatness, and geometric tolerances of each part meet assembly requirements.
Parts such as lens barrels, internal support frames, and guide rails, in particular, require extremely high precision, and aluminum die-casting has a natural advantage in this area.
(3) Good Heat Dissipation Performance
Modern cameras are equipped with high-pixel sensors and high-performance processors, and prolonged shooting generates a lot of heat. Poor heat dissipation can lead to reduced image quality, increased noise, and even automatic shutdown of the machine.
Aluminum alloy has excellent thermal conductivity, and die-cast structural parts are often used for:
Sensor heat dissipation base plate
Internal heat dissipation frame of the lens
Its rapid heat dissipation characteristics can effectively protect the core components of the camera, improve stability and service life, which is one of the reasons why many high-end cameras use metal parts.
(4) Good Appearance and Texture
A metal body has always been a symbol of professional cameras and high-end lenses. Aluminum die-cast parts can achieve a high-quality texture and luster through processes such as spraying, anodizing, and electrophoresis, while also offering advantages in wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
Compared to plastic parts, aluminum alloy casings:
Have a better metallic feel
Offer a more high-end visual effect
Are more in line with the positioning of professional-grade products
Therefore, many brands will definitely use aluminum die-cast structural parts in their high-end series to enhance the overall quality.
(5) Enables complex integrated structures
Aluminum die casting supports the integration of multiple structures in a single part, such as:
Studs
Heat sinks
Reinforcing ribs
Mounting slots
Threaded holes
Support frames
This means manufacturers can reduce the number of parts, lower assembly costs, and improve structural stability. This degree of design freedom is difficult to match with other manufacturing methods.
(6) Better suited for outdoor and complex environments
Photography activities often take place outdoors, and equipment needs to withstand vibration, drops, temperature changes, and even humid environments. Aluminum die-cast parts possess:
High strength
High stability
Corrosion resistance
Strong fatigue resistance
They can effectively protect internal structures and electronic components, reducing wear and tear during long-term use.
Camera accessory manufacturers prefer aluminum die casting because it combines multiple advantages such as lightweight, high strength, high precision, excellent heat dissipation, controllable cost, and design flexibility. For the camera industry, which requires compact structures and extremely high reliability, aluminum die casting is almost the most suitable manufacturing process. Whether it's high-end professional cameras, action cameras, or consumer-grade cameras, aluminum die-cast parts play an irreplaceable role in their structure.
4. Should Camera Structural Components be Made of Aluminum Die-Casting or Plastic?
In camera manufacturing, the material of structural components directly affects the product's durability, weight, strength, heat dissipation performance, and appearance. As cameras continue to develop towards lightweight, high-performance, and professional designs, there are generally two main choices for structural components: aluminum die-casting and plastic. Both have their advantages, but are suitable for different scenarios and needs. So, is aluminum die-casting or plastic more suitable for camera structural components?
(1) Characteristics of Aluminum Die-Casting Structural Components
1) High Strength and High Durability
Aluminum alloy has stronger mechanical strength than plastic, and can better resist external impact, bending, and fatigue damage caused by long-term use.
Suitable for: camera body, lens barrel, base, and other load-bearing or protective components.
2) Excellent Heat Dissipation Performance
Cameras contain high-heat components such as sensors, processors, and power modules. Aluminum alloy naturally has good thermal conductivity.
Advantage: Prevents problems such as stuttering, noise, and crashes caused by high temperatures.
3) Strong High-Precision Molding Capability
Aluminum die-casting can form complex structures in one go, with good dimensional consistency, suitable for the precise internal structure of cameras.
4) Higher Appearance Quality
Metal bodies have a higher quality feel and can be treated with oxidation, sandblasting, and painting, suitable for high-end cameras.
5) Higher Cost, but Suitable for Mid-to-High-End Products
Aluminum die-casting molds are more expensive, and the processing steps are more complex, but the finished product has strong performance and a long lifespan.
(2) Characteristics of Plastic Structural Components
1) Low Cost, Suitable for Mass Production
Plastic injection molding molds are cheaper and faster, and the cost is far lower than aluminum die-casting.
2) More Significant Weight Reduction
Although aluminum alloy is also lightweight, plastic is even lighter, suitable for products that are extremely sensitive to weight.
3) More Freedom in Structural Design
Plastic is easy to mold and can be advantageous in integrated structures and snap-fit designs.
4) Poor Heat Dissipation Capability
This is a fatal weakness of plastic and cannot be used in high-heat areas.
5) Weaker Strength and Durability
It is prone to aging and deformation with long-term use, and its performance deteriorates in high-temperature and humid environments.
6) Average Appearance Quality
Plastic surfaces are more prone to wear than metal, and the feel and quality are not as good as aluminum alloy. Excellent heat dissipation performance.
(3) Comparison table of camera structural parts selection: aluminum die-casting vs. plastics (such as ABS, PC, nylon, etc.)
| Comparison Dimensions | Aluminum Die Casting | Plastic (Injection Molding) |
| Material Characteristics | 1. High strength and rigidity 2. Excellent thermal conductivity 3. High temperature resistance (above 200℃) 4. Heavier weight |
1. Lightweight (density approximately 1/3 of aluminum) 2. Good insulation 3. Corrosion resistant 4. Lower rigidity, easily deformed |
| Process Complexity | 1. High mold cost (requires steel molds) 2. Long production cycle 3. Complex post-processing (e.g., CNC machining, anodizing) |
1. Lower mold cost (aluminum or steel molds) 2. Fast molding (seconds to minutes) 3. Complex structures can be integrally molded |
| Cost | 1. High unit cost (material + processing) 2. Suitable for large-scale production to reduce costs |
1. Low unit cost (especially for large quantities) 2. More economical for small batches |
| Accuracy and Surface Quality | 1. Good dimensional stability (shrinkage rate 0.5-0.7%) 2. Surface requires post-processing (e.g., sandblasting, electroplating) |
1. Higher shrinkage rate (0.5-2.0%), requires design compensation 2. Surface can be directly textured or high-gloss finished |
| Application Scenarios | 1. Load-bearing components (e.g., lens mounts, brackets) 2. Heat dissipation components (e.g., hot zones of the machine body) 3. High-end models |
1. Housings, decorative parts 2. Lightweight structural components 3. Low-cost or portable models |
| Environmental Adaptability | 1. High temperature resistance, impact resistance 2. Easily conductive (requires insulation treatment) 3. May oxidize (requires surface protection) |
1. Poor weather resistance (easily aged by UV light) 2. Easily brittle at low temperatures 3. Good insulation |
| Environmental Protection and Recycling | 1. 100% recyclable, but high energy consumption for melting |
1. Some plastics are recyclable (e.g., ABS), but difficult to degrade |
5. Camera Aluminum Die-Casting Parts FAQ
Q1: What are camera aluminum die-casting parts?
A1:
Camera aluminum die-casting parts are structural or functional components obtained by injecting molten aluminum alloy at high speed into a precision metal mold, followed by rapid cooling and shaping. They are commonly used in camera body frames, lens mounts, gimbal accessories, mounting brackets, guide rails, etc. Aluminum die-casting technology allows for the one-time molding of complex shapes, offering high dimensional accuracy and excellent surface quality. It is suitable for mass production and is currently the mainstream manufacturing method for many camera structural components.
Q2: What are the advantages of camera aluminum die-casting parts compared to plastic parts?
A2:
The main advantages include:
(1) Higher strength: Aluminum alloy has higher rigidity and impact resistance, providing better protection for internal precision electronic components.
(2) Excellent heat dissipation performance: Metal conducts heat far better than plastic, allowing for rapid dissipation of heat generated by sensors, CPUs, etc.
(3) Structural stability: Less prone to deformation and shrinkage during long-term use, maintaining reliability even in high or low temperature outdoor environments.
(4) Premium feel: The metallic appearance gives a more premium feel, enhancing the overall quality of the camera.
Q3: What are the main application areas of camera aluminum die-casting parts?
A3:
Including but not limited to:
Camera casings and body frames
Lens structural components and lens barrel mounts
Cold shoe mounts, tripod mounting bases
Gimbal and motorized slider accessories
Battery compartment structural components
Heat sinks, heat dissipation brackets, etc.
Aluminum die-casting parts can cover almost all critical components requiring load-bearing, connection, fixing, or heat dissipation.
Q4: Do aluminum die-casting parts affect camera weight?
A4:
Aluminum alloy is slightly heavier than magnesium alloy, but still much lighter than steel. By optimizing the structure, controlling wall thickness, and using hollow designs, a balance between lightweight and high strength can be achieved. Many lightweight cameras (such as mirrorless cameras) still widely use aluminum die-cast structural components because they combine strength with appropriate weight, contributing to stability and anti-shake performance.
Q5: How is the heat dissipation performance of camera aluminum die-casting parts?
A5:
Excellent. Aluminum alloys have high thermal conductivity, effectively dissipating heat generated during the operation of image sensors, processors, and WiFi modules. This is especially important for applications such as video recording, long exposures, and 4K/8K recording, reducing the triggering of overheating protection and improving camera stability.
Q6: Are aluminum die-cast parts prone to corrosion? How can corrosion resistance be enhanced?
A6:
Aluminum itself has a natural oxide film, providing good corrosion resistance. To further enhance it, the following methods can be used:
Powder coating/painting
Anodizing treatment
Electrophoretic coating
Anti-corrosion coating
These processes not only improve oxidation resistance but also enhance appearance and wear resistance.
Q7: What are the common surface treatment methods for camera aluminum die-cast parts?
A7:
Common treatment methods include:
Sandblasting
Anodizing
Powder coating
Brushing
Electrophoresis
CNC precision machining to enhance appearance
These processes can achieve different visual effects such as matte, glossy, and brushed metal finishes.
Q8: Can aluminum die-cast parts meet the requirements of high-precision camera structures?
A8:
Yes. Modern aluminum die-casting molds have high precision and small molding errors. Coupled with subsequent CNC precision machining, they can achieve:
±0.01–0.02 mm accuracy
One-time molding of complex structures
Stable manufacturing of thin-walled parts (less than 1 mm)
Therefore, it is very suitable for lens structural parts and connectors that require extremely high dimensional accuracy, coaxiality, and flatness.
Q9: What are the common quality problems of camera aluminum die-cast parts?
A9:
Common problems include:
(1) Porosity and shrinkage cavities: May be caused by insufficient pressure or poor mold venting.
(2) Deformation: Caused by uneven cooling or unreasonable wall thickness design.
(3) Surface defects: Mold wear and uneven coating can cause scratches and flow marks.
(4) Dimensional deviation: Caused by improper mold design and processing control.
These problems can be effectively solved through mold optimization, pressure parameter adjustment, and CNC precision machining.
Q10: Are aluminum die-cast parts suitable for mass production? What about the cost?
A10:
They are very suitable. The advantages of aluminum die casting lie in its one-time molding process, resulting in high speed and stability, making it particularly suitable for products with high production volume and numerous structural components, such as cameras.
The cost structure mainly includes:
Mold costs (high initial investment)
Aluminum material costs
Processing and surface treatment costs
However, as production volume increases, the cost per unit decreases rapidly, making it a preferred manufacturing method in the camera industry.
Q11: Are aluminum die-cast parts environmentally friendly? Are they recyclable?
A11:
Aluminum die-cast parts are 100% recyclable, and the performance of the recycled material remains stable, making it one of the most environmentally friendly metal manufacturing methods currently available. Compared to plastic parts, which require the disposal of chemical waste, aluminum alloy is more environmentally friendly and sustainable.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体

 +0086-18158459905
+0086-18158459905